
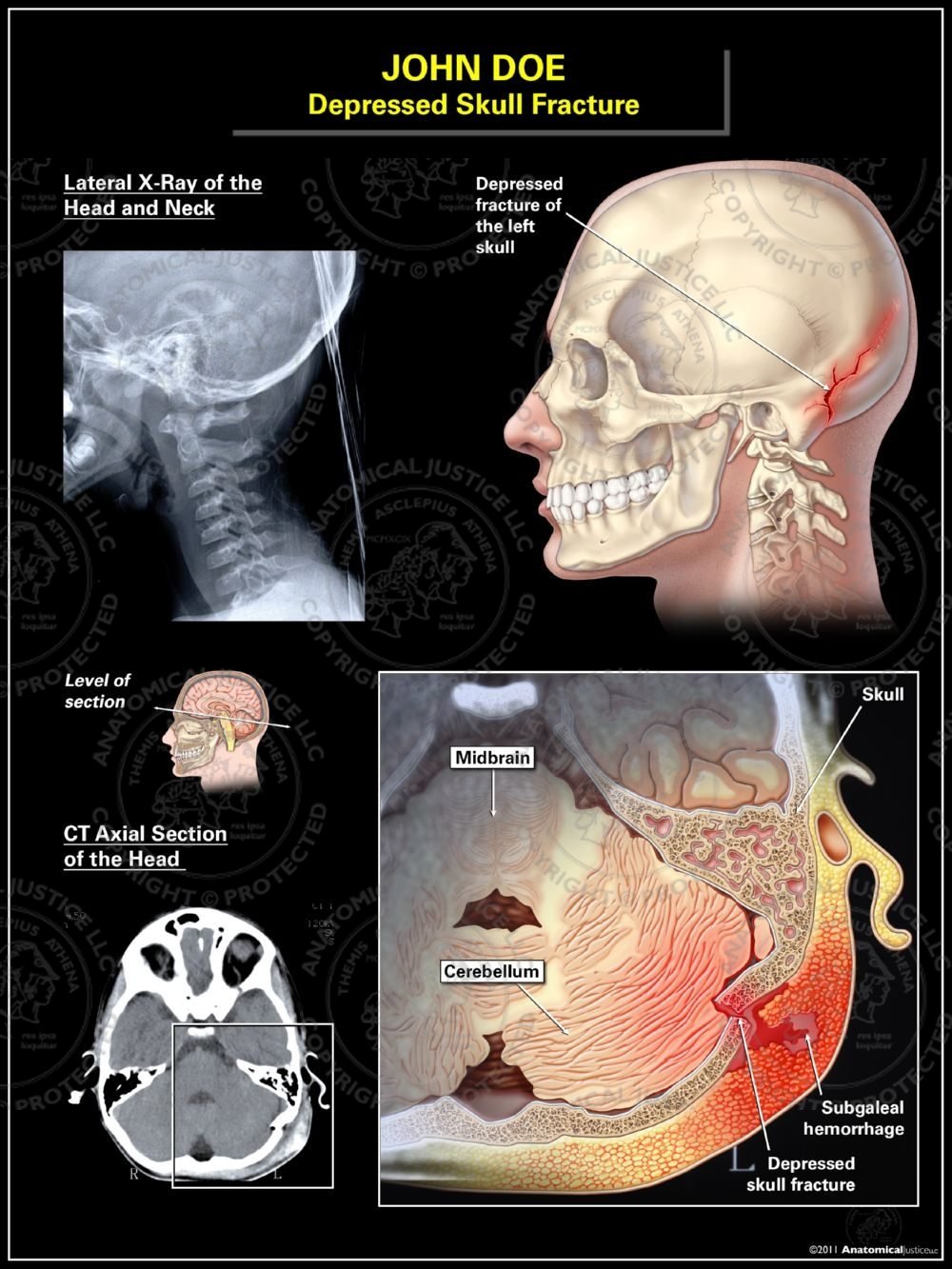
This can happen in car accidents, from falls or shaken baby syndrome. Diffuse axonal injuries (DAI) are fairly common and are usually caused by shaking of the brain.When trauma is not the cause, the most common causes are high blood pressure in adults, bleeding disorders, the use of medications that cause blood thinning or illicit drugs. Bleeding that occurs inside the brain (also called intraparenchymal hemorrhage) can sometimes occur spontaneously. Contusions may occur with skull fractures or other blood clots such as a subdural or epidural hematoma. A contusion causes bleeding and swelling inside of the brain and around the area where the head was struck. Contusions, or intracerebral hematoma, are bruises on the brain.They are sometimes, but not always, associated with a skull fracture. These can form from a tear in the veins that go from the brain to the dura, or from a cut on the brain itself. Subdural hematomas occur when a blood clot forms underneath the skull and dura but outside of the brain.Epidural hematomas are usually associated with a skull fracture. They usually come from a tear in an artery that runs just under the skull called the middle meningeal artery. Epidural hematomas occur when a blood clot forms underneath the skull but on top of the dura, the tough covering that surrounds the brain.The different types of ICH include the following: These can range from mild head injuries to quite serious and potentially life-threatening injuries. The different types are classified by their location in the brain. There are several types of ICH, or blood clots, in or around the brain. These patients usually require close observation in the hospital. They may also have clear fluid draining from their nose or ears due to a tear in part of the covering of the brain. Patients with this type of fracture frequently have bruises around their eyes and a bruise behind their ear. Basilar skull fractures are the most serious type of skull fracture, and involves a break in the bone at the base of the skull.

These fractures are more often seen in newborns and older infants.
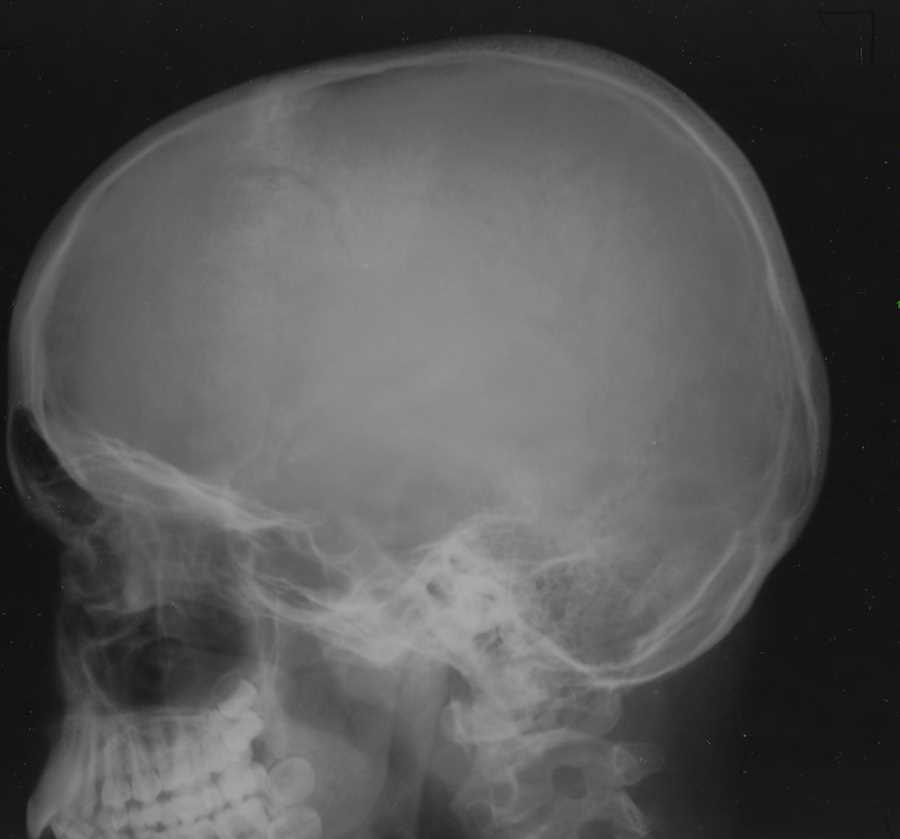
In this type of fracture, the normal suture lines are widened. The sutures are the areas between the bones in the head that fuse when we are children.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
